The Relationship Between Triangles And Elliott Wave Theory
Triangles in Elliott Wave Theory are like puzzle pieces in the market’s story, showcasing consolidation before explosive moves. These patterns within the larger wave structure guide traders in identifying potential breakouts. Understanding their types and behaviour isn’t just helpful—it’s game-changing for crafting precise trading strategies. Dive in to explore how triangles unlock market secrets and refine forecasting. Are triangle patterns a reliable tool in wave analysis? Visit bitindexai.top, which helps traders access experts who shed light on such technical dynamics without overcomplicating the process.
The Anatomy of Triangles in Elliott Wave Theory
Understanding the Shape and Dynamics of Triangles
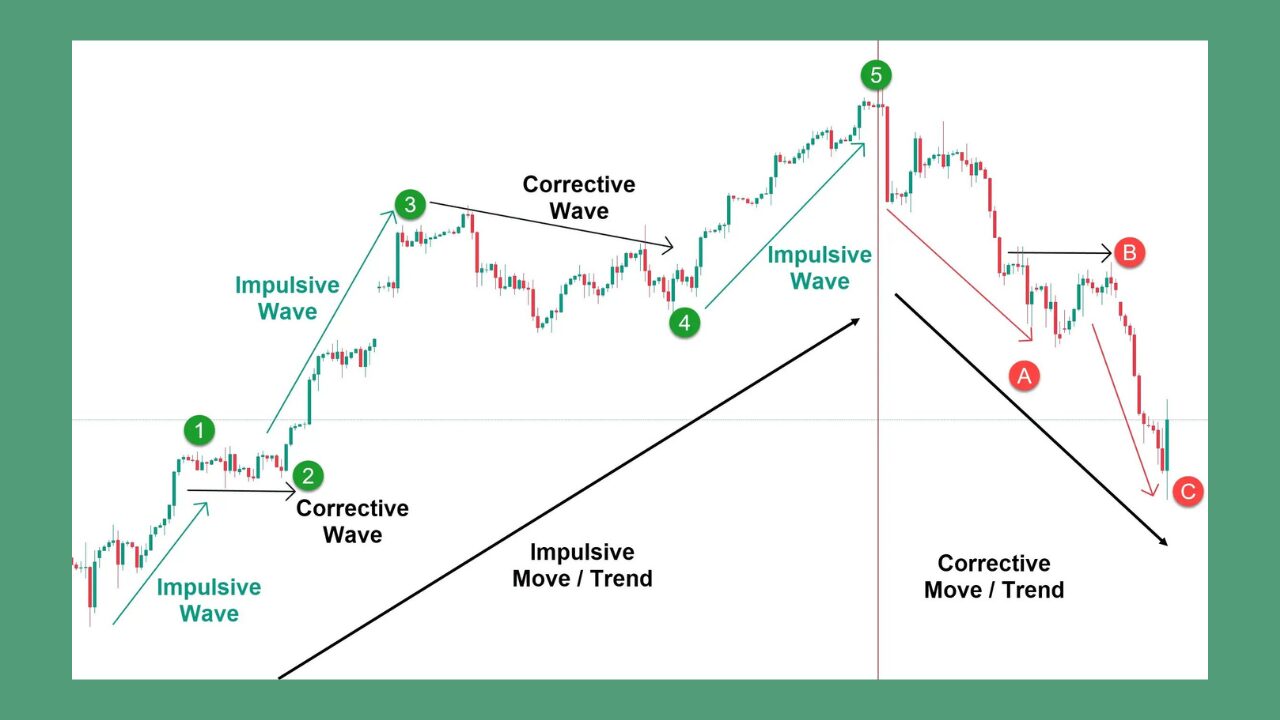
Triangles in Elliott Wave Theory are chart patterns that indicate price consolidation. These formations consist of five waves, A, B, C, D, and E, oscillating within converging trendlines. Depending on market conditions, these structures can either contract or expand. Imagine a spring being compressed, storing energy until it’s ready to release—this is what triangles reflect in market movements.
The Different Types of Triangles
Triangles are classified into symmetrical, ascending, descending, contracting, and expanding. Symmetrical triangles have balanced forces of buyers and sellers, forming neat converging lines. Ascending triangles show bullish potential, with a flat resistance level and a rising support line.
Descending triangles, on the other hand, suggest a bearish sentiment, with resistance sloped downward. Expanding triangles display greater market volatility, with trendlines moving apart. Understanding these variations helps traders align their strategies effectively.
Why Wave Count Matters in Triangles?
Triangles always consist of five sub-waves, which must adhere to the Elliott Wave principle. These waves represent corrective patterns, typically forming during market pauses. Correctly counting these waves is critical for accurate predictions.
Misinterpreting them can lead to flawed decisions, like entering or exiting trades prematurely. For example, during the 2008 financial recovery, failing to identify a triangle’s completion phase led some traders to miss profitable opportunities.
Triangles as Continuation Patterns in Wave Progression
Where Triangles Appear in the Elliott Wave Sequence
Triangles frequently occur in waves four or B of the Elliott Wave sequence. In wave 4, they act as resting points, allowing the market to digest prior gains before the final impulsive wave. In wave B, they function as a corrective phase, signalling temporary market consolidation. Recognizing this placement allows for precise forecasts of market movement.
Triangles as Road Signs for Market Trends
Triangles signal that the market is preparing for a significant move, usually in the direction of the preceding trend. They act as a warning for traders to prepare for action. For instance, a triangle in a bullish trend often means the market will break upward. Picture this as a race where runners pause to catch their breath before sprinting to the finish line—this is how triangles behave.
How Triangles Help Navigate Uncertainty
Triangles provide clarity during periods of uncertainty by narrowing price movements. This compression creates predictable breakout points, which are essential for planning trades. For example, during the 2016 commodity price fluctuations, triangles in gold charts gave traders hints about upcoming trends, enabling them to act confidently. Monitoring volume during triangles can also indicate the strength of potential breakouts, a critical factor for decision-making.
Trading Implications of Triangles in Elliott Wave Analysis
Using Triangles to Predict Market Moves
Triangles are often used to anticipate strong market breakouts. Traders analyze the final E wave and the breakout’s direction to confirm their entries. However, waiting for breakout confirmation minimises risks like a significant price close above or below the triangle’s boundaries. Rushing into trades without clear signs is like leaping before looking—it often ends badly!
Managing Risk Effectively with Triangles
Risk management is vital when trading triangles. Placing stop-loss orders slightly outside the triangle’s boundaries is a common approach. For instance, if selling an ascending triangle in a bullish trend, a stop-loss order can be set below the triangle’s lowest point. Such measures protect against unexpected reversals while maximizing profit potential.
Real-Life Applications of Triangle Patterns
Triangles have been pivotal in trading significant indices and commodities. During the 2020 market recovery, symmetrical triangles in technology stocks hinted at upcoming rallies. Traders who recognized these patterns were able to ride the momentum effectively.
This highlights why triangles are such a valuable tool for any trader aiming to predict market direction confidently. Think of them as a compass—helpful in keeping your trading strategy on track even in choppy waters.
READ MORE
Conclusion
Triangles are more than patterns; they’re roadmaps in market analysis, signalling pauses and impending shifts. Their strategic placement in Elliott Wave Theory helps traders anticipate trends with clarity. Decoding their structures and implications can transform hesitation into confident decisions. Master triangles, and watch your trading game elevate to a new level.
